Enrolling in Medicare after age 65
Not everyone enrolls in Medicare when they are initially eligible. Many decide to retire later in life, some for financial reasons and others for the enjoyment they receive from being part of the workforce. Make sure you know what comes next when you do prepare to retire and start looking for health coverage on your own.

Plan on retiring later?
Fill out this form and we’ll temporarily remove you from our marketing outreach and only contact you with important reminders about Medicare deadlines as you get closer to retirement.
Medicare eligibility and enrollment
Most people become eligible for Medicare at age 65, but not everyone will retire at that time. Here are some important facts to consider if you are retiring later.
- If you have employer-provided health insurance, you may choose to delay enrolling in Medicare Part B, or medical insurance, to avoid paying your employer premiums and Medicare premiums.
- When you’re ready to retire or lose your employer coverage, you can enroll in Medicare during an eight-month special enrollment period (SEP).
- You have 63 days after your employer coverage ends to enroll in Medicare Part D or Part C without penalty.
- This special enrollment period begins the month after you retire or lose your employer coverage. It’s important to enroll during this timeframe to avoid paying penalties.
- To enroll in Medicare Part A or Part B, contact the Social Security Administration online, by phone or in person.
- It’s best to start learning about Medicare and your coverage options at least four to five months before you plan to retire. You can start by requesting our no-obligation “Understanding Medicare” guide.
Frequently asked questions
The answer depends on your individual circumstances. Most people who’ve worked and paid taxes are eligible for premium-free Medicare Part A when they turn 65, even if they still have health insurance from an employer. Since there is usually not a premium, signing up for Medicare right away would be beneficial.
However, Medicare Part B does have a monthly premium. If you don’t want or need Part B, you can delay your enrollment. However, you may be better off enrolling in Medicare when you’re first eligible so that you avoid late enrollment penalties.
You can delay enrollment in Medicare Part B or in a Part D prescription drug plan—and delay the monthly premiums—but you may pay a higher premium once you decide it’s time to enroll.
For more information on potential fees, visit medicare.gov.
If you want or need to work past 65 and you are currently receiving healthcare coverage from your employer (with at least 20 other plan members), you might choose to delay enrolling in Medicare with no penalties. For more information on how to avoid penalties, visit medicare.gov.
The benefits of choosing a Medicare Advantage plan
When you do decide to retire, look to get all the benefits you deserve. Original Medicare, or Medicare Part A and Part B, won't cover all of your medical expenses. Most people should consider adding additional coverage, like a Medicare Advantage plan. Medicare Advantage plans often include additional benefits beyond Original Medicare, such as prescription drug coverage (Part D), vision, dental, hearing and wellness benefits. You’ll want to compare plan options for differences in cost, coverage and provider network.
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to pick a plan. You can enroll through Medicare Plan Finder or directly with an insurance company offering Medicare Advantage plans. WellSense offers several Medicare Advantage plans that include hospital, medical and prescription drug coverage.
Additional resources
Calculate your retirement age
Do your research
Search available Medicare Advantage plans at Medicare Plan Finder or on our Shopping page.
Get more help
Medicare 101
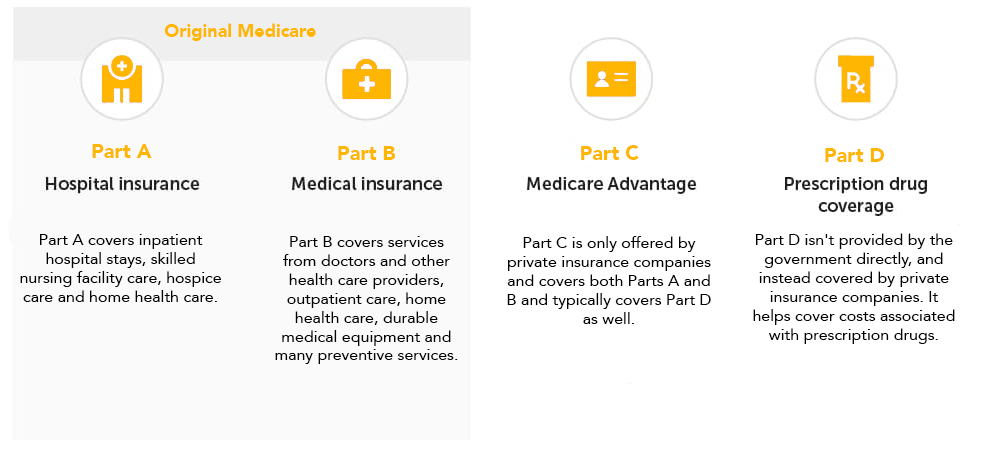
Original Medicare is made up of two parts, Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance). Medicare Part C (also known as Medicare Advantage) is offered by private insurance companies such as WellSense to provide extra benefits that Original Medicare doesn't offer. A separate Medicare drug plan, known as Part D, can be joined to help supplement prescription costs.
Understanding the Medicare parts
Medicare is divided into four parts: A, B, C, and D, with each part providing partial coverage to help pay for healthcare expenses.
Original Medicare vs. Medicare Advantage
Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage, though both regulated by the federal government, are offered through different entities. Original Medicare is covered by the government and contains Parts A and B. Medicare Advantage (Part C) is offered by private insurance companies and covers both Parts A and B and typically covers Part D as well.
Costs
| Original Medicare | Medicare Advantage |
| After meeting your deductible, you typically pay a coinsurance of 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for services covered by Part B. | The out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare services can differ between plans, with some plans having lower or higher costs for specific services. |
| To receive Part B coverage, you are required to pay a monthly premium. Additionally, if you opt for Medicare drug coverage through Part D, you will also have a separate monthly premium for that. | You're responsible for the Part B monthly premium and possibly the plan's premium. Certain plans have a premium of $0 and can assist with paying all or a portion of your Part B premium. The majority of plans offer Medicare drug coverage (Part D). |
| What you pay out-of-pocket has no yearly limit, unless you supplement your Original Medicare with Medigap, the Medicare Supplement Insurance. | Each plan has a cap on the total amount you have to pay out-of-pocket every year for services covered by Medicare Part A and Part B. Once you hit your plan’s cap, you won’t have to pay anything for covered Part A and Part B services for the remainder of the year. |
| To help cover out-of-pocket costs such as coinsurance, you have the option to enroll in Medigap. Additionally, you can utilize coverage from a previous employer or union, or Medicaid. | You don't need Medigap. |
Doctors and hospitals
| Original Medicare | Medicare Advantage |
| You are free to choose any doctor or hospital across the United States that accepts Medicare. | For non-emergency care, typically, you can only utilize healthcare providers who are in the plan’s service area and network. |
| For most situations, a referral to a specialist isn't needed. | Some plans may require a referral to see a specialist. |
Coverage
| Original Medicare | Medicare Advantage |
| Original Medicare generally includes coverage for medically necessary services and supplies provided in hospitals, doctors' offices, and other healthcare facilities. However, certain services like routine exams, most dental care, and eye exams are not typically covered by Original Medicare. | Medicare plans are required to provide coverage for all the medically necessary services that are covered under Original Medicare. Additionally, some plans may offer additional benefits beyond what Original Medicare covers, such as dental, vision, and hearing services. |
| Drug coverage can be obtained through a separate Medicare drug plan known as Part D. | Most plans include the Medicare drug coverage known as Part D. |
| Original Medicare typically doesn't require prior approval for coverage of most services and supplies. | For many plans, prior approval is often required for coverage of certain services or supplies. |
Eligibility and enrollment
Original Medicare (Parts A and B)
Most individuals are eligible for an Original Medicare plan (Parts A and B) around their 65 birthday. Other eligibilities are being a U.S. citizen or legal resident for five consecutive years, being eligible for Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board, and having paid into Medicare through payroll taxes.
Enroll in Original Medicare by applying online through the Social Security Administration, visiting a local Social Security office or calling the Social Security office or the Railroad Retirement Board.
Your Initial Enrollment Period begins three months before you turn 65 and ends three months after you turn 65. This period lasts for 7 months total.
If you miss your Initial Enrollment Period for Medicare Parts A and B, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty when you do enroll.
Your Medicare card
Once enrolled in Medicare, you will receive a Medicare card with a unique number. Remember to bring it with you to all medical appointments.
You are leaving the WellSense website
You are now leaving the WellSense website, and are being connected to a third party web site. Please note that WellSense is not responsible for the information, content or product(s) found on third party web sites.
By accessing the noted link you will be leaving our website and entering a website hosted by another party. Please be advised that you will no longer be subject to, or under the protection of, our privacy and security policies. We encourage you to read and evaluate the privacy and security policies of the site you are entering, which may be different than ours.